Uterus removal surgery: cost, duration and step by step

- Why is uterus removal surgery necessary?
- Surgical treatments for uterus removal
- Post-operative of uterus removal surgery
- Cost of Uterus Removal Surgery
- Request a surgical assessment consultation
- A uterus removal surgery, also known as hysterectomy, is a surgical intervention that depending on the quantity of organs removed, it will be a partial, total or radical hysterectomy.
- Hysterectomy may be carried out with several surgical techniques, However, the main goal is the removal of the uterus.
- Depending on the technique performed, the duration, admission days, and recovery time after an uterus removal surgery will vary.
The uterus is an organ of the female reproductive system that has a pear shape and is located between the bladder and the rectum.
The fertilised egg is implanted in the womb, resulting in pregnancy. Therefore, a woman who undergoes womb removal will not be able to become pregnant.
Uterus removal surgery or hysterectomy is a surgical intervention in which the womb is removed, due to a series of diseases associated with this organ. Depending on the degree of the disease and its reach, there’ll be the need for a partial, total or radical hysterectomy.
But what does each technique consist of?:
- Partial uterus removal: also known as subtotal hysterectomy, this involves the removal of the body of the uterus.
- Total uterus removal: the corpus and cervix and cervix are removed.
- Radical uterus removal: performed when the corpus of the uterus, cervix, upper vagina, and all lymph nodes and ducts need to be removed.
- Total uterus removal plus double adnexectomy: in cases where a radical hysterectomy has been performed but, in addition, it is necessary to remove the fallopian tubes and the two ovaries.
An uterus removal surgery can be partial, total and radical depending on the associated pathology.
There are various problems that can occur in the uterus, so it is not always necessary to remove the uterus completely. From a clinical perspective, the causes for which a hysterectomy is usually performed can be divided according to whether they are benign or malignant.
Below you can read about the main reasons why uterus removal is usually performed.
Why is uterus removal surgery necessary?
Throughout history, hysterectomy has been the most and least frequently recommended option, depending on the continuous advances in this surgical area. The introduction of therapeutic tools has displaced the surgical option in favour of less invasive, i.e. less radical treatments. However, there are a number of diseases that make uterus removal necessary.
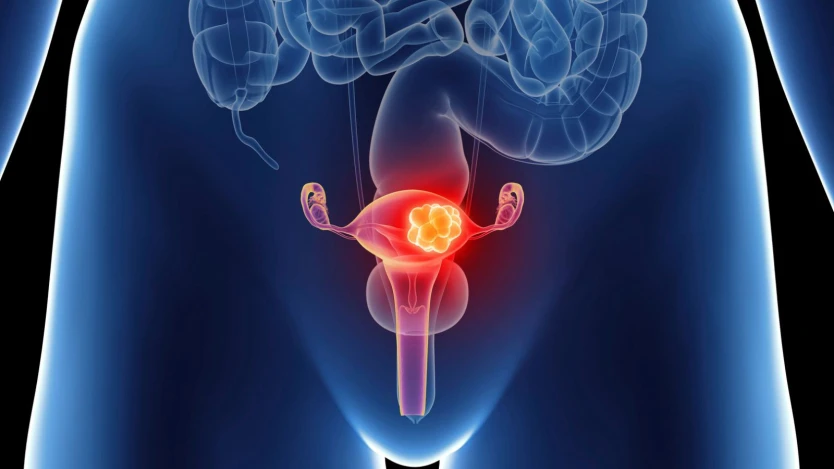
Generally, the most common profile of women who undergo hysterectomy is usually patients between 35 and 55 years old with medical conditions in the uterus area.
Uterus removal surgery is necessary in the following cases:
- Genital prolapse: it is one of the most frequent reasons to perform this surgery. In this case, the muscles of the pelvic floor are weakened and cause the uterine sagging. This condition is usually common in women of advanced age, and also women who have given birth multiple times.
- Uterine fibroids: it is another frequent medical condition in which an hysterectomy may be recommended. Fibroids are abnormal growths, which are generally benign in nature. Although there are other surgeries, such as myomectomy, which can remove them without removing the uterus, hysterectomy is the recommended intervention for older women who no longer want to have children and want to completely eliminate the possibility of fibroids recurrence.
- Abnormal bleeding: it’s a type of uterine bleeding in which there is no injury or organic cause that justifies an alteration in the menstrual cycle, in regards to its duration and intensity.
- Adenomatosis: it is a benign disease which consists of the formation of endometrial tissue in the same muscular layer as that of the uterus, resulting in a thickening of the uterus.
- Cervical neoplasia: neoplasia is pre-cancerous growth that occurs in the cervix of the uterus and that usually our immune system eliminates. However, in some cases, the neoplasia evolves and surgery is needed.
- Endometrial neoplasia: as with cervical neoplasia, endometrial neoplasia, in the best of cases, will not pose a danger to the patient. However, hysterectomy is the appropriate option in more serious situations such as endometrial cancer.
If an uterus cancer has been developed and the disease has spreaded, an uterus removal surgery will be highly recommended
Uterus removal surgery is an intervention quite common in the gynaecological area, since this type of treatment allows to prevent and put a solution to disease such as the cervix cancer, uterus cancer or other similar conditions.
In any of these cases, before making the decision, it is advisable to consult a gynaecological specialist to determine whether the disease requires a hysterectomy, the type of hysterectomy and the route by which it is to be performed.
We remind you that Operarme offers you a first surgical assessment consultation with one of our specialists.

Do you need hysterectomy surgery?
Request a free and immediate appointment with our specialists in Gynecology
Surgical treatments for uterus removal
Hysterectomy is the surgical intervention in which the uterus is removed and in some cases, also the removal of its surrounding parts in the pelvic cavity.
As aforementioned, there are several conditions that may happen in the uterus area and end up requiring a hysterectomy surgery.
In the following section we’re going to classify hysterectomy surgery in different techniques according to the approach in the procedure: abdominal, vaginal, laparoscopic and Da Vinci Robot.
Uterus removal surgery is the number one gynaecological surgical procedure in Spain. Among these surgeries, 65% are performed via the abdominal route, 25% via the vaginal route and around 10% via laparoscopy. As for robotic hysterectomy, although it is the latest surgical technique in the gynaecology world, it is the technology with the most intraoperative and postoperative benefits for uterus removal surgery.
Among hysterectomy techniques we can find four different types of intervention:
Vaginal Hysterectomy
Vaginal hysterectomy consists of the removal of the uterus through the vagina. In this type of intervention, the surgeon accesses the interior of the pelvic cavity through a small incision in the superior area of the vagina to remove the womb and/or the surrounding organs.
Uterus removal surgery via vaginal is performed in the following way:
- A pericervical incision is made anterior and superior to the vagina so that the surgeon can locate the bladder, ureters and the ligaments that attach them to the womb for removal.
- A pericervical incision is made posterior to the vagina, so that it joins with the previous incision and the rectovaginal space can be accessed.
- The supravaginal septum, i.e. the fibres that hold the uterus and vagina in place, is sectioned. In this way, part of the uterus is freed.
- The Douglas sac is opened, through which the uterosacral ligaments are located and dissected.
- Through the anterior opening, the peritoneal cavity is entered and the ovarian appendages, fallopian tubes, arteries, etc. are located.
- The uterine vessels are clamped, the uterus is turned over and extracted, with appropriate haemostatic control.
- Next, a culdoplasty is performed to prevent the vaginal vault from prolapsing.
- Finally, the peritoneum is closed layer by layer, in the same way as the vagina.
Vaginal hysterectomy is performed under general anaesthesia.
Abdominal hysterectomy
Abdominal hysterectomy consists of the removal of the uterus and its surrounding parts (uterine cervix, ovaries, etc) through an incision in the abdomen area.
Through this approach, the surgeon can access the pelvic cavity.
Most of the time, a patient who undergoes abdominal hysterectomy presents a pathology not suitable for any other surgical technique like a very enlarged uterus with fibroids, extensive endometriosis with abdominal and ovarian involvement or an inflammatory pelvic disease, among others.
Thus, the removal of the womb consists of the following steps:
- The surgeon will make an incision in the abdomen, through which the abdominal cavity will be reached.
- Once there, the surgeon will place a retractor to keep the incision open and proceed to check the organs of the pelvic cavity.
- After locating the uterus and grasping it with two forceps, the surgeon will localise the elements that nourish the uterus. In this case, the round ligament is sutured and the section of the ureter is avoided.
- The bladder is then located in order to separate it from the uterus by dissection.
- In the same way that the uterus has been located, the cervix is located and sectioned.
- Once the womb has been removed and the cervix has been closed, the rest of the structures of the cavity are checked to ensure that they are in perfect condition.
- Finally, saline solution is used to eliminate any bleeding that may have occurred and both cavities are closed.

Assess your uterus problem with our surgeon
Request a free and immediate surgical consultation with our specialist in Gynecology.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy
Laparoscopic technique is recommended, most of all, in patients with non-extended benign pathologies. In comparison to the rest of the techniques, laparoscopy presents a low rate of complications and less time for recovery.
The laparoscope is a surgical instrument that allows visualisation of the abdominal-pelvic after introducing it through a small incision.
This tool consists of a light source and a camera that is connected to a television monitor, from where the surgeon can see inside the patient.
The team of surgeons introduce the necessary instruments to perform the entire step-by-step procedure of the womb removal operation:
- First, the patient will be positioned facing the ceiling with her legs open, so that the abdominal wall and hip remain at the same level.
- Next, general anaesthesia is administered and the patient is monitored.
- The bladder is catheterised with a Foley catheter and an intrauterine manipulator is placed to allow manipulation of the uterus from the outside.
- The laparoscopic instruments are inserted, with one trocar being used to inflate the abdomen for a clear view of all the organs, and the other two for precise manipulation of the abdominal viscera.
- Although the step-by-step of laparoscopic hysterectomy has variations, in general, it is a very similar technique to abdominal removal. The most striking difference is that instead of clamping, cutting and ligating the uterus, as in abdominal hysterectomy, it is done by coagulation of the surrounding structures.
- The next step is to section or open the cul-de-sac above the uterosacral ligaments, allowing the uterus to be released and separated from any nearby structures.
- First the round ligaments are coagulated, then the opening of the anterior and posterior peritoneum, then the pelvic infundibulum, and finally the uterine vessels. The uterus is then removed.
- Morcellation is used: a technique that facilitates the removal by partitioning the abdominal mass, when the uterus exceeds 300 grams.
- Finally, the vagina is closed with a continuous suture and, if the surgery is 100% laparoscopic, with separate stitches or continuous suture.

Robot Da Vinci Hysterectomy
This robotic technology offers the most safe option for patients who face complex surgical interventions such as neoplasias of the uterus, cervix or endometrium.
Da Vinci technology was developed in order to be able to operate in places where access is difficult or even impossible, for example in war situations. Therefore, it is not necessary for the surgeon to be at the patient's bedside to perform womb removal surgery.
Da Vinci robot consists of three parts: a fixed robot with the robotic arms that come into action during the surgery, the console through which the surgeon sees inside the patient, and the image processing system that captures all the information in three-dimensional images.
Thus, the surgery of womb removal with Da Vinci Robot consists of the following:
- Once the anaesthesia has taken effect, the trocars are placed on the abdomen.
- The robot is then placed between the patient's legs, at 45 degrees, for better vaginal access.
- From the monitor, the surgeon observes all the pelvic structures and performs a purging in the cavity.
- From the console, the surgeon performs an electrocoagulation and sections the round ligament.
- The surgeon then opens the peritoneum to dissect it and gain access to the anterior aspect of the vagina without bladder injury.
- The uterine artery and uterosacral ligaments are dissected and cut with coagulation, allowing the uterus to be released.
- The vagina is opened and the uterus is removed through the vagina.
- Finally, a resorbable suture is performed.
Post-operative of uterus removal surgery
Uterus removal surgery, also known as an hysterectomy, is an intervention that depending on the technique performed will have a different duration.
As aforementioned, there are different types of surgery for uterus removal, and each one of them has different intra and post-operative characteristics.
However, depending on the patient's circumstances, partial, total or radical removal will be performed. Therefore, it is not only the technique that has an influence, but also the percentage of organs adjacent to the womb that need to be removed.
Post-operative of Abdominal hysterectomy
The surgery for abdominal hysterectomy has a duration of 60-80 minutes. Once it has been completed, the patient is taken to a recovery room where she will stay until all the effects of the anaesthesia have disappeared.
Once the anaesthesia has been eliminated completely from the organism, the patient will be taken to her room. In this hospital room she will remain there for up to 3 days.
During the first hours after hysterectomy, the diet will be 100% drip bed.
Twelve hours after surgery, the patient will begin to drink liquids and, if tolerated, a semi-liquid diet may be administered 24 hours after the intervention. If everything goes well, after 48 hours, the digestive function will be completely recovered and a soft diet will be given.
It is important during the first 24 hours to fully rest, in order to ensure fixation of the anatomical structures that have been sutured. In addition, it is appropriate for the patient to be admitted for 2 to 4 days and to be discharged when a normal diet is available. Therefore, the hospital stay is approximately 3 days.
In regards to recovery, in the case of abdominal surgery it can take up to 6 to 8 weeks.

Post-operative of Vaginal hysterectomy
Vaginal hysterectomy surgery lasts between 45 and 80 minutes. As in other surgeries where general anaesthesia is applied, the patient will be taken to a recovery room afterwards until the medication is fully eliminated from her organism. Finally, she will be taken to the hospital room where she will remain until discharge.
Regarding diet, the patient will start with a single dropper diet until reaching solids in a progressive manner. Depending on the tolerance in the change from one diet to another, the progression will be faster or slower. However, 24-36 hours after the hysterectomy, digestive function will have completely recovered and, with it, the diet with solid food.
After 48-72 hours of hysterectomy surgery, the patient will leave the hospital
Recovery at home will normally take between 2 and 4 weeks. However, the time will vary depending on the individual characteristics of each patient.
Post-operative of Laparoscopic hysterectomy
The surgery of Laparoscopic Hysterectomy takes between 60-80 minutes. It is the less invasive technique, and the admission and stay in the hospital is reduced to 1-2 days.
As in the other techniques, once the patient is accommodated in her private room she will start a progressive diet, from a single dropper diet to solid food.
Once she’s discharged from the hospital, the patient will start recovery at home following the instructions from the surgeon. Total recovery can take up to 1-2 weeks.

Post-operative of Da Vinci Robot Hysterectomy surgery
Da Vinci Robot uterus removal surgery, or robotic hysterectomy, lasts 60 - 80 minutes. After the surgery is completed, the patient will be transferred to the recovery room until all the anaesthetic from the surgery has worn off.
As for the length of hospital stay, the patient will be admitted in the hospital for 1 to 2 days.
Da Vinci Robot is a technology capable of operating on serious diseases, such as neoplasia, with a minimally invasive technique.
Therefore the surgery duration, hospital stay and recovery stage will depend on the reason for which the patient has undergone surgery.
However, even if the surgery is complicated, the Da Vinci Robot allows for a recovery time of between 1 and 6 weeks.
Cost of Uterus Removal Surgery
The cost of uterus removal surgery, independently of the technique to be performed, is a fixed price in which all the resources and services needed for the safe performance of the surgery are included.
Below you can find a comparison of the prices of uterus removal, depending on the technique used:
- Abdominal Hysterectomy Surgery has a fixed cost of 5.190 €
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Surgery starting from 6.190 €
- Vaginal Hysterectomy Surgery starting from 4.690€
- Robotic Hysterectomy for Cervical Neoplasia has a fixed cost of 22.600€
Request a surgical assessment consultation
Operarme offers you a first surgical assessment consultation with the specialist, free of charge. In this first consultation, the gynaecologist will determine whether your situation requires surgical intervention and also which type of surgery is appropriate for your case.
If you want to book your appointment with the specialist, you can call us on +34 91 141 33 56 and check if we collaborate with a hospital in your city to perform the removal of the uterus.
You can also click on the following image or fill in the contact form and a member of the Operarme Patient Service Team will contact you immediately to solve your questions and/or schedule your consultation.

Get your surgery date with Operarme
Request now a free consultation with our specialists in Gynecology and set a date for your uterus removal intervention.
Medical disclaimer: All the published content in Operarme is intended to disseminate reliable medical information to the general public, and is reviewed by healthcare professionals. In any case should this information be used to perform a diagnosis, indicate a treatment, or replace the medical assessment of a professional in a face to face consultation. Find more information in the links below: