Types of knee surgery: Arthroscopy and Arthroplasty
- When should knee surgery be performed?
- Knee arthroscopy
- Recovery after knee arthroscopy
- Joint replacement (Arthroplasty)
- Recovery after knee replacement surgery
- Bibliography
- Source information
- Frequent Questions
When should knee surgery be performed?
Knee surgery is a surgical procedure that allows for the replacement or reconstruction of severely damaged parts of the joint.
This intervention becomes necessary when the cartilage in the joint begins to wear down due to diseases such as osteoarthritis and the bones rub against each other. In this case, the type of surgery performed would be knee arthroplasty, i.e. the replacement of the joint with a knee prosthesis.

Knee arthroscopy can also be performed when one of the parts of the joint is injured, for example:
- Torn meniscus
- Damaged or torn cruciate ligaments
- Inflammation or injury to the lining (synovial membrane) of the joint
- Misaligned kneecap
- Loose cartilage or bone fragments in the joint
- Baker's cyst. A swelling that forms behind the knee that, in some cases, is a result of inflammation from other causes, such as arthritis.
- Cartilage defect
Knee surgery is performed to relieve pain and improve quality of life.
Although it is true that there are non-surgical treatments and analgesics that help to alleviate the pain and discomfort caused by the poor condition of the joint, on many occasions the only effective solution is surgery.
As you have read, within the surgical possibilities, there are several ways to proceed. Here are the different types of knee surgeries that are performed.
Knee arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint (arthro-) is visualised (-scoped) using a small camera.
This technique allows doctors to have a clear view of the inside of the knee, facilitating the diagnosis and treatment of different problems such as: meniscus injury and cruciate ligament tears.
Meniscus injury
- The surgeon makes small incisions in the knee. Through these incisions, the surgeon inserts a saline solution to increase the joint space and remove any cloudy fluid, improving the surgeon's visibility through the arthroscope.
- He inserts the arthroscope and will inspect the inside of the knee to confirm the meniscus injury and make sure there is no other injury to the ligaments or bone. After making sure of this, he will proceed with the meniscus surgery.
- Through the remaining incisions, the surgeon inserts the surgical instruments needed to repair the meniscus.
This repair can be carried out using two different techniques, depending on the characteristics and severity of the injury.
Partial meniscectomy
This consists of the removal of the free part of the meniscus that has become detached due to the meniscal tear. Total meniscectomy is not recommended (although sometimes necessary) because it causes future problems of premature osteoarthritis.
Meniscal suture
This involves suturing the damaged part of the meniscus. It is the most common choice for young people and athletes, as it has very good long-term results.
Meniscus surgery by arthroscopy takes between 30 and 60 minutes. Normally, the patient can go home the same day, although it is advisable to stay in hospital overnight to ensure the success of the surgery.

Cruciate ligament reconstruction
- The specialist makes small incisions in the knee through which the cannulas and instruments that make up the arthroscope are introduced.
- Once inside, a small incision is made in the anterior aspect of the knee in order to extract the tissue and make the new ligament.
- The tissue is prepared with the exact measurements and reinserted into the tunnels made, which are locked with the corresponding screws and at the exact tension.
The duration of cruciate ligament reconstruction is 30 - 60 minutes.
After the surgery is completed, hospitalisation for at least 2 days is necessary to ensure that there are no postoperative complications.
Recovery after knee arthroscopy
After discharge from hospital, 2 days after the intervention, it will be necessary to continue exercises at home or in a rehabilitation centre until full mobility is achieved.
Physiotherapy can help many people regain movement and strength in the knee after arthroscopic cruciate ligament surgery.
Walking is possible within 24 hours of surgery, with the aid of crutches, mobilising the knee within 12-24 hours, bending the knee to a right angle at one week and achieving full mobility between the 2nd and 4th week.
Full recovery occurs between weeks 6 and 8.
An important thing to remember is not to do any heavy physical work until recovery. Similarly, contact sports should not be started before 6 months. All this is conditioned by the need for the transplanted bone to be sufficiently remodelled to withstand any load.
Joint replacement (Arthroplasty)
Knee arthroplasty or joint replacement is a procedure in which the damaged knee joint is removed and replaced with prosthetic metal, ceramic and/or plastic components.
It is usually performed when the muscles, cartilage and bones that make up the knee are irreparably damaged.
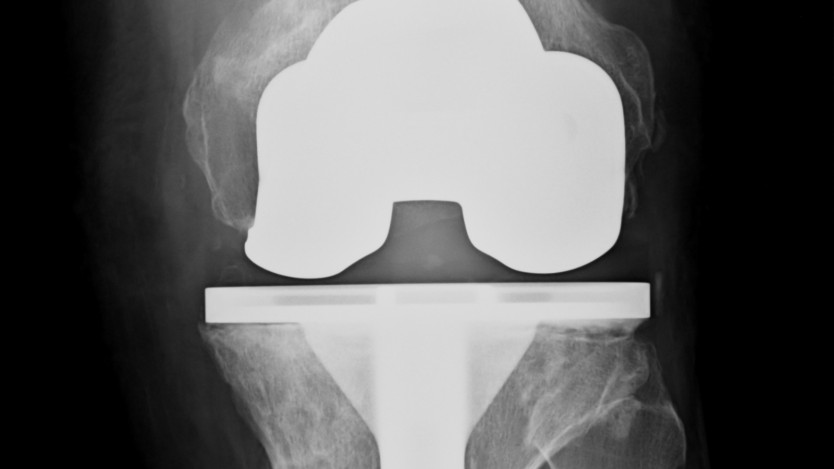
Knee arthroplasty is therefore performed as follows:
- The specialist makes a 20 to 25 centimetre incision in the front of the knee until reaching the bone area.
- The orthopaedic surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone.
- Then, the surgeon prepares the femur and tibia with bone cement, if it will be used.
- Right after, the surgeon will place the new metal, plastic, and ceramic implants to restore alignment and function to your knee:
-
- Femoral component
- Tibial component
- Insert, which will allow favourable gliding of the femoral component during movement.
- Patellar component. This component will only be placed if it needs to be replaced, and then repair all the muscles, tendons and ligaments that have been affected.
If only part of the knee needs to be replaced, the arthroplasty is partial. However, when damage is observed over a large part of the joint, total knee arthroplasty is the recommended surgery.
The duration of the knee replacement surgery depends on the characteristics of each patient and the severity of the deformity, but usually ranges between 2 and 3 hours of surgery.
After the surgical intervention, it will be necessary to stay in hospital for 4 - 5 days, depending on the patient's evolution.
Recovery after knee replacement surgery
Admission after knee arthroplasty is 4 to 5 days. During admission, the specialists make sure that everything has gone well and that it is safe to go home.
Rehabilitation starts as soon as possible in the hospital, with the help of the nursing team. They will teach you some exercises for your knee that you should do to improve and avoid postoperative complications.
During rehabilitation at home after knee replacement surgery, there are three very important points to bear in mind to avoid possible complications and in turn improve recovery times:
- Care of the surgical wound with the intention of avoiding possible infection.
- Care for the diet. Eating a balanced diet is important to avoid being overweight as this may cause damage to the new prosthesis.
- Exercises for the knee. Starting to move and walk is perhaps the most important part of knee replacement surgery rehabilitation, as improving and strengthening muscle mass will help maintain the stability of the new joint.
During the first few months it is important to follow the exercises provided by the physiotherapist to the letter, although some patients also choose to do the daily exercises with a personal physiotherapist or at a rehabilitation centre.
The final recovery after total knee replacement surgery varies between 3, 6 and 12 months.
The time will depend directly on the previous deformity of the joint, the patient's own characteristics and the intensity of the post-operative rehabilitation.

Do you need knee replacement surgery?
Request a free and immediate appointment with our specialists
Bibliography
- Arthritis Foundation. (s. f.). Cirugía de la rodilla. Recuperado 2020, de https://espanol.arthritis.org/espanol/tratamientos/cirugia/cirugia-rodilla/
- Medline Plus. (2020, 7 mayo). Reemplazo de la articulación de la rodilla. https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/ency/article/002974.htm
- (2012, octubre). Reemplazo total de rodilla (Total Knee Replacement) - OrthoInfo - AAOS. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/es/treatment/reemplazo-total-de-rodilla-total-knee-replacement
Dr. Antonio Rebollo Marina
Médico Asistencial en Centro Médico Caser
Nº colegiado: 282834715

Medical disclaimer: All the published content in Operarme is intended to disseminate reliable medical information to the general public, and is reviewed by healthcare professionals. In any case should this information be used to perform a diagnosis, indicate a treatment, or replace the medical assessment of a professional in a face to face consultation. Find more information in the links below:
Frequent Questions
-
When is knee surgery performed?
Although it is true that there are non-surgical treatments and analgesics that help to alleviate the pain and discomfort caused by the poor condition of the joint, on many occasions the only effective solution is surgery.
Thus, the causes for which knee surgery is resorted to are:
- Meniscus injury
- Repair of cruciate ligament
- Removing pieces of torn cartilage
- Removal of synovial tissue
- Diseases such as arthritis, osteoarthritis, etc.
- Read more
-
How long will it take me to recover after knee arthroscopy?
The recovery time varies between 3, 6 and 12 months.
This will be directly influenced by the previous deformity of the joint, the patient's own characteristics and the intensity of the postoperative rehabilitation.
-
How long does knee arthroscopy take?
Knee arthroscopy for both meniscus injuries and cruciate ligament reconstruction lasts between 30 - 60 minutes.
-
How long will it take to return to normal life after knee arthroplasty?
The time it will take you to fully recover will vary between 1 and 3 months, depending on the intensity of the rehabilitation and the surgical technique used.