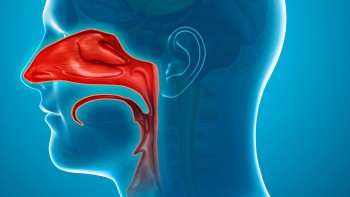
Turbinate Inflammation: what it is, causes, symptoms and treatment

- Turbinate inflammation
- What causes turbinate inflammation?
- What are the symptoms of turbinate inflammation?
- Diagnosis for turbinate inflammation
- Treatments for turbinate inflammation
- Radiofrequency treatment to solve turbinate inflammation
- Request your surgical assessment consultation with Operarme
- Inflammation of the turbinates leads to hypertrophy of the turbinates and, therefore, nasal obstruction that prevents the air we breathe from passing through.
- Among many of the causes of turbinate inflammation are allergic processes such as allergic rhinitis.
- Currently, radiofrequency surgical treatment for turbinate inflammation is one of the most commonly used.
Turbinate inflammation
Turbinate inflammation involves turbinate hypertrophy, resulting in an excessive increase in the volume of the turbinates. Turbinate hypertrophy is an inflammation that can sometimes be intermittent but, if not treated properly, can become a chronic inflammation of the turbinates, causing persistent nasal congestion.
But, what are turbinates and what do they do?
The turbinates are a nasosinusal structure located inside our nose. It has three turbinates on both sides of the nasal cavity and separated by the septum.
The nasal turbinates are in a staggered position and, depending on their size, we locate the upper, middle and lower turbinates, the latter being the one with the greatest volume and, therefore, the one that can cause nasal obstruction.
This nasosinusal structure is covered with mucous membranes that have a large number of blood vessels, which are very sensitive.

Do you need turbinates reduction surgery?
Request a free and immediate appointment with our specialists in Otorhinolaringology
Regarding the function of the turbinates, they are responsible for directing the flow of air inside the nasal cavities. Their functions are responsible for improving the quality of our breathing. Among them, we find:
- Humidifying the air that reaches the lungs.
- Filtering the air we breathe.
- Warming the air so that it does not reach the lungs cold.
The inferior turbinates regulate airflow by congesting and decongesting the cavernous tissue, i.e. by increasing and reducing its size. Thus, when there is turbinate inflation, or turbinate hypertrophy, there is a nasal obstruction that does not allow airflow to pass through.

Colds, allergies, smoking and/or alcohol intake are factors that can alter the functioning of the turbinates and cause inflammation or hypertrophy. In addition, the blood vessels contained in the structure are very sensitive.
However, in the following section, you can find out more about the causes that affect the size of the turbinates, so we invite you to read on.
What causes turbinate inflammation?
Turbinate inflammation involves turbinate hypertrophy, i.e. an enlargement of the mucous membranes due to nasal obstruction. As mentioned above, if this inflammation is not treated properly, it can become chronic over time.
Allergic processes, such as allergic rhinitis, are the cause and reason for this turbinate disorder, among many others. Thus, the turbinates can be altered by:
- Hormonal change. Drugs, pregnancy or puberty, are factors that can disrupt hormone production and cause an increase in the volume of the membranes and turbinates, leading to nasal obstruction.
- Advanced age. Over the years, the body degrades and a number of diseases can contribute to swollen turbinates, making it difficult to breathe through the nose due to nasal obstruction and abundant secretion of mucus.
- Overweight. Obesity means a smaller lung volume, so breathing will be more of an effort. Being overweight increases the likelihood of a number of abnormalities in the nasal passages, such as turbinate hypertrophy or inflammation.
- Exposure to polluted air. Being in places with a toxic environment or low temperatures puts more strain on the airways. This leads to an increase in the size of the turbinates, as well as other parts exposed to the same stress.
- Tobacco and/or alcohol intake. These two lifestyle habits increase the likelihood of turbinate inflammation. The functioning of the structure degrades until it collapses and causes nasal obstruction.
- Acute or chronic sinusitis. Inflammation and involvement of the sinuses can lead to turbinate inflammation. This disease can alter the size of the turbinates and obstruct the nasal passages, allowing you to breathe only through your mouth.
- Deviated nasal septum. A deviated septum can lead to the need to exert more effort to breathe. This is the cause of turbinate inflammation, as well as turbinate alteration.
- Pharmacological treatment. Some treatments with steroids or nasal application can cause inflammation of the nasal structure and lead to turbinate swelling or hypertrophy.
What are the symptoms of turbinate inflammation?
Inflammation of the turbinates is a hypertrophy or alteration of the turbinates. The nasal structure can be affected intermittently or, if pharmaceutical treatment has no effect, it can become chronic, causing obstruction in the nasal cavities.
The symptoms of turbinate inflammation are diverse and can sometimes be asymptomatic or, on the contrary, very annoying. Some of them are:
- Permanent nasal congestion
- Physical tiredness
- Apnoea and sleep disorders
- Difficulty breathing through the nose
- Hearing problems and discomfort
- Nosebleeds
- Loss of smell
- Facial pain
- Snoring
As mentioned above, these symptoms may be intermittent or not present at all. However, lack of treatment or inadequate treatment can turn turbinate inflammation into a chronic pathology.
Therefore, if you have any of these symptoms, Operarme advises you to visit a specialist to diagnose the main cause of the discomfort.
Diagnosis for turbinate inflammation
The diagnosis of turbinate inflammation is made after examination of the nasal cavities. As we have already mentioned in previous sections, turbinate inflammation is a hypertrophy of the turbinates.
Therefore, in order for the ENT specialist to make an appropriate diagnosis for your situation, he or she will examine the nasal cavities, normally by rhinoscopy.

This endoscopic technique is minimally invasive. It involves the use of a rhinoscope, an instrument that separates the nasal ala from the septum and increases the field of vision. To complement the intervention, the specialist will use a frontal mirror and a light to improve vision inside the nasal cavity. This test lasts approximately 5 to 10 minutes.
Rhinoscopy is classified according to the technique used. These can be:
- Anterior rhinoscopy. In this test, the otorhinolaryngologist will operate through the nose to see the elements of the anterior portion of the nostrils such as the mucosa, the nasal vestibule, the inferior turbinates and sometimes the middle turbinates, i.e. the roof of the nostrils and the choanae. During the anterior rhinoscopy, you will be in an armchair, with your head straight, your mouth closed and breathing normally, calmly and through your nose.
- Posterior rhinoscopy. In this case, the doctor performs the test through the mouth to see the back part of the nostrils, such as the upper turbinate, the middle turbinate, the tail of the lower turbinate and the vomer. This test makes use of a speculum, a front mirror and an external light source. You will be seated in an armchair, with your head straight and slightly forward, so, when the test is performed through your mouth, you will keep it open, with your tongue relaxed inside it and, in the same way, breathing calmly through your nose.
No preparation is necessary before performing rhinoscopy. However, it is advisable to clean the nasal passages beforehand, using saline solutions.
In anterior rhinoscopy, where the nasal route is used, a vasoconstrictor can be used to reduce the volume of the turbinates. On the other hand, if the posterior rhinoscopy causes nausea, a topical anaesthetic will be applied during the examination, although this is not usual.
At the consultation, the doctor will want to find out about your lifestyle, your symptoms, previous illnesses, etc. All this information will be useful to make a more accurate diagnosis and, thus, propose the most appropriate solution, in the form of treatment.
Treatments for turbinate inflammation
Inflammation of the turbinates or turbinate hypertrophy involves an increase in the volume of the inferior turbinates, causing nasal obstruction. Since each person has a different case, each case of hypertrophy requires a particular treatment, depending on the cause that is producing this blockage in the nasal cavities.
Treatments to alleviate turbinate inflammation are classified according to their type. Among them, we highlight the natural treatment to prevent inflammation, treatment with medication and surgical treatment, as well as radiofrequency surgery to reduce turbinate inflammation. Below we explain what each of them consists of:
Preventive treatment
The correct treatment for turbinate inflammation will be carried out after finding out the main cause of nasal congestion. Preventive treatment may work if your problem is related to allergies or substances that have irritated the area. However, it is important to see your doctor to find out what has caused the allergy and turbinate inflammation.
Some of the safety measures to carry out this treatment consist of:
- Remove pollen from your home.
- Remove dust.
- If you have a pet, remove its dandruff.
Drug treatment
Medication is usually the most common treatment to reduce turbinate inflammation. Depending on the drugs, these will be classified as corticosteroid nasal sprays, allergy medications. In addition, try to avoid exposure to environmental irritants. All these contribute to the reduction of turbinate swelling, as well as to the improvement of nasal breathing.
Medical treatment is not always effective, so other options may be indicated to solve turbinate inflammation, as well as its main causes and symptoms.
In this case, when medical treatment has not been effective, turbinate hypertrophy can become chronic and the ENT specialist will recommend surgical treatment as the only effective solution.
Surgical treatments
Turbinate inflammation involves several surgical treatments to reduce or remove the part of the bony structure that causes nasal obstruction. Treatments include:
- Turbinoplasty. Also known as surgical fracture, it modifies the position of the turbinates. The surgeon intervenes with endoscopic tools and accesses the inside of the nostrils until reaching the turbinates. Turbinectomy reduces the size of the turbinate by sectioning a small part of it.
- Turbinectomy. Unlike turbinoplasty, with this technique all or part of the turbinate is removed, sectioning the tissue necessary to eliminate the nasal obstruction. Turbinectomy also makes use of endoscopic tools.
- Radiofrequency. This is the most common technique for reducing the size of the turbinates. Radiofrequency is made up of electrodes that are inserted through the nostrils and placed on the turbinates. Electromagnetic energy circulates through the electrodes and increases the temperature of the tissues without damaging the adjacent structures in order to solve turbinate inflammation.
- Laser. This procedure cauterises the nasal mucosa to reduce the size of the turbinates and reduce nasal obstruction.
Currently, radiofrequency surgical treatment is one of the most commonly used to solve nasal obstruction caused by swollen turbinates. For this reason, and so that you can learn more about what this surgical procedure consists of, we explain below how it is performed.
Radiofrequency treatment to solve turbinate inflammation
Radiofrequency treatment for turbinate reduction is a minimally invasive and painless procedure that lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. It is performed on an outpatient basis, i.e. on the day of the operation you can go home, always taking into account the doctor's assessment.
When you are ready for surgery, you will go to the operating theatre where you will meet the surgeon, the anaesthetist and a member of the nursing team. Once you are on the operating table, the operation will begin:
- First, you will be given a local anaesthetic to numb the area.
- After the anaesthesia has taken effect, the surgeon will insert the tip of a needle-tipped terminal through the nostrils and puncture the front of the inferior turbinate.
- This tool is connected to a radiofrequency equipment that transmits energy to the turbinate tissue to reduce the volume of the turbinates, making room for air to enter through the nostrils.
- Once the size of the turbinates has been reduced, the surgeon will remove the instrument from the nasal cavity and you will be taken to the recovery room to recover from the anaesthesia.
Once all the anaesthetic has worn off, you have recovered from its effects and the surgeon has checked that everything has gone perfectly, you can leave the hospital.
Recovery after turbinate hypertrophy surgery
If swelling and mucous inside the nose appear after the operation, do not worry. This is most common. However, as the days go by, everything will disappear. Therefore, to help the recovery process, we advise you to follow the instructions of the doctor who has dealt with your case:
- Nasal lavage. After the operation, it is necessary to keep the operated area clean. Therefore, during the recovery stage you should wash your nose with physiological saline solution or saline water to promote healing and prevent subsequent infections.
- Avoid heat. Keep away from areas with high temperatures, and avoid exercising or taking aspirin, which can contribute to the development of haemorrhages.
Full recovery from turbinate hypertrophy surgery is complete in 10-15 days after the operation. However, you will notice the improvement as the days go by.
Request your surgical assessment consultation with Operarme
If your nasal structure presents a clear case of turbinate inflammation, you can request a free surgical assessment consultation with one of our specialists in Otolaryngology.
Our patient counselling team will be at your disposal to answer any questions you may have and/or to arrange the surgical assessment consultation. You can request your appointment by calling at +34 91 141 33 56, or by clicking on the image below:

Do you need turbinates reduction surgery?
Request a free and immediate appointment with our specialists in Otorhinolaringology
Medical disclaimer: All the published content in Operarme is intended to disseminate reliable medical information to the general public, and is reviewed by healthcare professionals. In any case should this information be used to perform a diagnosis, indicate a treatment, or replace the medical assessment of a professional in a face to face consultation. Find more information in the links below: