10 things you didn't know about hysterectomy
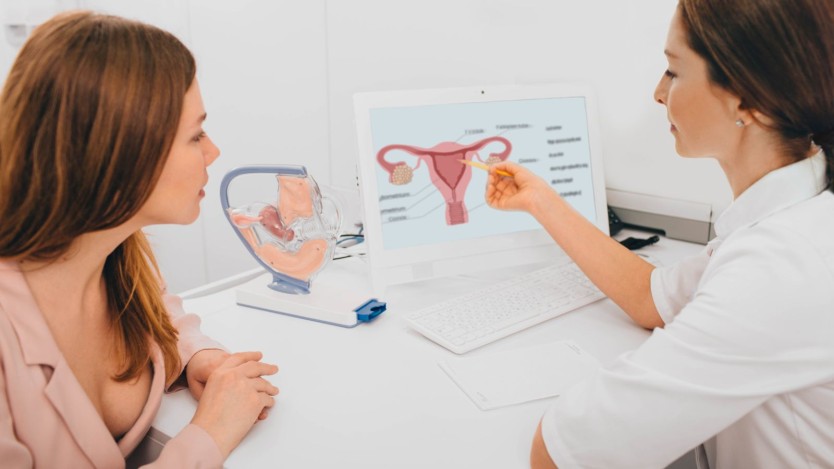
- Hysterectomy surgery
- What you need to know about hysterectomy and its effects on women's health
- Request a free assessment consultation for Hysterectomy surgery
Hysterectomy surgery
- A hysterectomy is the partial, total or radical removal of a woman's uterus.
- It is one of the most frequent surgeries in the gynaecological field, as it is a method for solving various conditions of the reproductive system.
- Hysterectomy is a complex operation, but there are no major complications, even if the method used varies. It is advisable to comply with all the necessary care during the postoperative period.
Hysterectomy surgery consists of the removal of a woman's uterus or womb; this type of operation may also involve the removal of other organs such as ovaries or fallopian tubes. This will depend on the type of problem with the reproductive structure and the doctor's recommendations.
Below we explain some aspects that we find interesting and important to know about the surgery and what it entails.

Do you need hysterectomy surgery?
Request a free and immediate appointment with our specialists in Gynaecology
What you need to know about hysterectomy and its effects on women's health
- After hysterectomy, most women report no adverse effects on sexual intercourse. They report more satisfactory intercourse, especially those women who before the surgery suffered from pain in the uterus or prolonged bleeding. Most women are able to have sexual intercourse as early as 6 weeks after surgery.
- Women who have a hysterectomy stop having periods, resulting in symptoms such as menopause.
- As with any operation, the removal of the uterus has its risks. Hysterectomy is a complex operation, but in most cases there are no complications. The most common problems that can occur are blood clots, infection, bleeding after the operation or problems during defecation. To reduce the chances of problems, it is important that the patient follows the instructions and care before and after the operation.
- During the first few days after the operation, specialists prescribe strong painkillers and recommend the patient to do gentle exercise such as walking during the first 24 hours after the operation.
- Admission to hospital after a hysterectomy can vary between 2 and 3 days, depending on the method by which the uterus was removed and the condition that the patient was suffering from.
- A hysterectomy may be performed when benign diseases related to the muscular layer of the uterus, the mucosa (endometrium), an altered position of the organ (descent of the uterus) or bleeding occur. However, such cases are rare compared to more serious conditions such as cancer of the uterus, cervix or ovaries.
- There are three methods of removing the uterus and these can be abdominal hysterectomy, vaginal hysterectomy and laparoscopic hysterectomy. The choice of method depends directly on factors such as the surgeon's experience, the size of the uterus and the type of disease to be treated.
- A hysterectomy is usually performed in conjunction with a complementary procedure called a salpingo-oophorectomy, in which the ovaries and fallopian tubes are also removed.
- Nowadays approximately 50% of hysterectomies are performed to treat Menorrhagia, a condition that consists of excessively heavy bleeding during the period and occurs mainly in women between 35-50 years of age.
- After a hysterectomy operation some women may experience feelings of loss, but in general this emotional reaction is temporary and disappears. But in most cases women feel increased health and improved quality of life.
Request a free assessment consultation for Hysterectomy surgery
If you have any questions about the hysterectomy process or you are thinking of having surgery with us, you can request a free surgical assessment consultation with our specialist in gynaecological surgery and obstetrics. You can request a surgical assessment consultation by clicking below:

Do you need hysterectomy surgery?
Request a free and immediate appointment with our specialists in Gynaecology
Medical disclaimer: All the published content in Operarme is intended to disseminate reliable medical information to the general public, and is reviewed by healthcare professionals. In any case should this information be used to perform a diagnosis, indicate a treatment, or replace the medical assessment of a professional in a face to face consultation. Find more information in the links below: